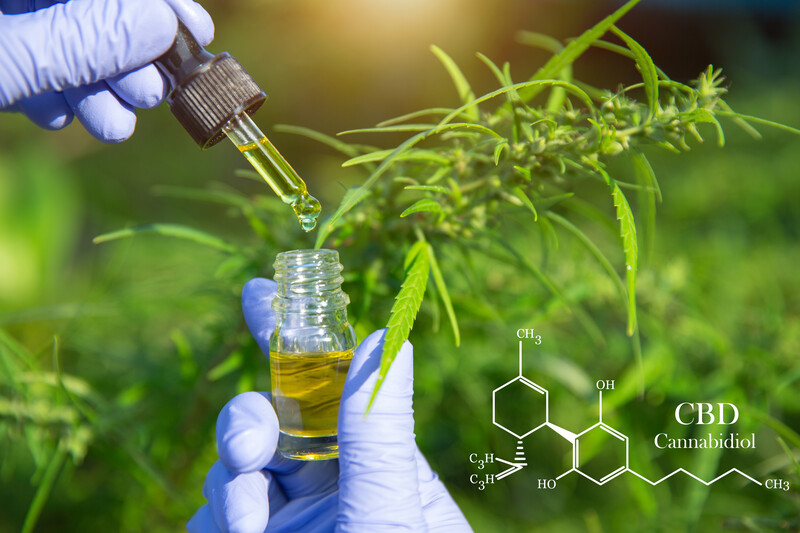
The effectiveness of medical cannabinoid in relieving and alleviating the symptoms of many conditions is being well documented in the research. One area of recent interest is cannabinoid’s antibiotic properties.
A January 2021 study published in the journal Communications biology (1) “present(s) a detailed evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of cannabidiol, the main non-psychoactive component of cannabis. (The authors of this study) confirm previous reports of Gram-positive activity and expand the breadth of pathogens tested, including highly resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Clostridioides difficile.”
Gram-positive bacteria are a class of bacteria that build up a thick membrane wall in their cells that make it difficult for antibiotics to get through. They are sometimes described as antibiotic resistant. In the study these highly resistant bacteria are listed as:
Staphylococcus aureus, a bacteria responsible for upper respiratory infections, pneumonia, and blood infections
Streptococcus pneumoniae, as its name suggests another class of bacteria responsible for upper respiratory infections and pneumonia.
and Clostridioides difficile or commonly called C Diff, a bacteria responsible for dangerous episodes of Watery diarrhea
In the study the research team suggests that their findings “demonstrate that cannabidiol has excellent activity against biofilms (a biofilm is a bacterial compound that can grow on a surface. It was first discovered as the plague and “bacterial” film that can grow on teeth), little propensity to induce resistance (the cannabinoid does not stimulate the bacteria to become resistant), and topical (skin application) efficacy. Multiple mode-of-action studies point to membrane disruption as cannabidiol’s primary mechanism. (The cannabidiol can get through the thick walls of antibiotic resistant bacteria). More importantly, (the study’s authors) report for the first time that cannabidiol can selectively kill a subset of Gram-negative bacteria that includes the ‘urgent threat’ pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea). Structure-activity relationship studies demonstrate the potential to advance cannabidiol analogs as a much-needed new class of antibiotics.”
The bacteria on teeth.
The study authors said that cannabidiol was particularly good at breaking down biofilms — the slimy build-up of bacteria, such as dental plaque on the surface of teeth — which help bacteria such as MRSA survive antibiotic treatments.
More research on MRSA
MRSA or Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is a particularly hard to treat bacterial infection because it is resistant to commonly used antibiotics.
In a statement from McMaster University researchers that coincided with the publication of their study “Uncovering the Hidden Antibiotic Potential of Cannabis” published in March 2020 in the journal American Chemical Society infectious diseases (2), the researchers noted: “that the chemical compound, or cannabinoid, called cannabigerol (CBG) is not only antibacterial but also effective in mice against a resilient family of bacteria known as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The research team found that CBG had antibacterial activity against drug-resistant MRSA. It prevented the ability of that bacteria to form biofilms, which are communities of microorganisms that attach to each other and to surfaces; and it destroyed preformed biofilms and cells resistant to antibiotics. CBG achieved this by targeting the cell membrane of the bacteria.”
Researchers excited by “untapped potential”
A July 2020 study published in the journal Antibiotics (3) calls medical cannabinoid in the form of Cannabis sativa a plant with untapped potential. They write: “It has an extensive metabolic profile and its medicinal properties should not be overlooked or overshadowed by its overuse as a recreational drug. Current antibiotic drugs have limited efficacy against Multidrug-resistant bacteria and their usage can be limited due to their toxicity for prolonged treatments; therefore, the discovery of an antimicrobial therapy of plant origin will no doubt be a great advancement in the field of anti-infectives.”
1 Blaskovich MA, Kavanagh AM, Elliott AG, Zhang B, Ramu S, Amado M, Lowe GJ, Hinton AO, Zuegg J, Beare N, Quach D. The antimicrobial potential of cannabidiol. Communications Biology. 2021 Jan 19;4(1):1-8.
2 Farha MA, El-Halfawy OM, Gale RT, MacNair CR, Carfrae LA, Zhang X, Jentsch NG, Magolan J, Brown ED. Uncovering the hidden antibiotic potential of Cannabis. ACS infectious diseases. 2020 Feb 4;6(3):338-46.
3 Karas JA, Wong LJ, Paulin OK, Mazeh AC, Hussein MH, Li J, Velkov T. The antimicrobial activity of cannabinoids. Antibiotics. 2020 Jul;9(7):406.































Recent Comments